Formidable Info About How Many Volts Are In 3-phase

Understanding 3-Phase Voltage
1. What Exactly is 3-Phase Power?
Ever wondered why some electrical things seem way more powerful than others? Like, why that industrial machine hums with authority while your phone charger just quietly does its job? A big part of that difference often comes down to the type of electrical power it uses. We're talking about the world of 3-phase electricity! Think of it as the electrical equivalent of having three super-efficient workers instead of one struggling to get the job done.
Single-phase power, which is what you usually find in your home, delivers power in a single, pulsating wave. Three-phase power, on the other hand, delivers three overlapping waves, resulting in a smoother and more consistent power supply. This makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications like running large motors, powering factories, and generally doing all the stuff that needs a serious electrical kick. Its like having a smoothly rotating engine versus a single piston firing intermittently.
Now, before your eyes glaze over, let's consider an analogy. Imagine trying to push a merry-go-round by yourself. It's tough, right? It starts and stops, and requires constant effort. Now, imagine three friends helping you, each pushing at different points around the circle. Much smoother, isn't it? That's essentially what 3-phase power does — it delivers continuous power, making it much more efficient.
So, why should you care? Well, even if you don't work in an industrial setting, understanding the basics of 3-phase power can help you appreciate the infrastructure that powers our modern world. Plus, it's a fun fact to whip out at parties. Just try not to put everyone to sleep! It is truly a hidden hero.
2. How Many Volts Are In 3-Phase Systems? The Nitty-Gritty!
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks. When we talk about "how many volts are in 3-phase," there isn't a single, universal answer. It depends on the specific application and the region you're in. Think of it like asking "how much does a car cost?". It relies on many factors.
In North America, common 3-phase voltages include 208V, 480V, and 600V. The 208V system is often found in commercial buildings, like offices and retail spaces, to power things like HVAC systems and larger appliances. The 480V and 600V systems are more common in industrial settings, where theyre used to run heavy machinery, manufacturing equipment, and other power-hungry devices. Imagine a gigantic metal-stamping machine or a robot arm welding car parts — those are likely powered by 480V or 600V 3-phase systems.
In Europe, you'll often see 400V systems as a standard. And in other parts of the world, you might encounter different voltage levels altogether. The key takeaway here is that 3-phase voltage isn't a one-size-fits-all situation. It's a variable that's tailored to the specific needs of the application.
It's essential to remember that working with 3-phase electricity can be dangerous. These systems carry high voltages and currents, so it's crucial to have proper training and use appropriate safety equipment. If you're ever unsure about anything, always consult a qualified electrician. Safety first, sparks later (hopefully never)!

Delving Deeper
3. Voltage Levels Explained
You might be wondering, "Why so many different voltages? Why not just pick one and stick with it?" Well, the answer lies in efficiency and cost. Higher voltages are more efficient for transmitting power over long distances, as they reduce current and minimize energy loss due to resistance in the wires. This is why power companies use very high voltages to transmit electricity from power plants to substations.
However, higher voltages also require more robust and expensive equipment, like transformers and insulation. For smaller applications, like powering a single machine in a factory, a lower voltage may be more cost-effective. It's all about finding the right balance between efficiency and affordability.
Think of it like this: a massive cargo ship is great for hauling tons of goods across the ocean, but it's not very practical for running errands around town. Similarly, a high-voltage 3-phase system is ideal for powering a large factory, but it would be overkill for powering a small office building. The voltage level is chosen based on the specific needs of the application.
Understanding the rationale behind different voltage levels can help you appreciate the complexity of electrical power distribution. It's not just about flipping a switch and getting power; it's about carefully engineering a system that delivers the right amount of power, safely and efficiently, to where it's needed.
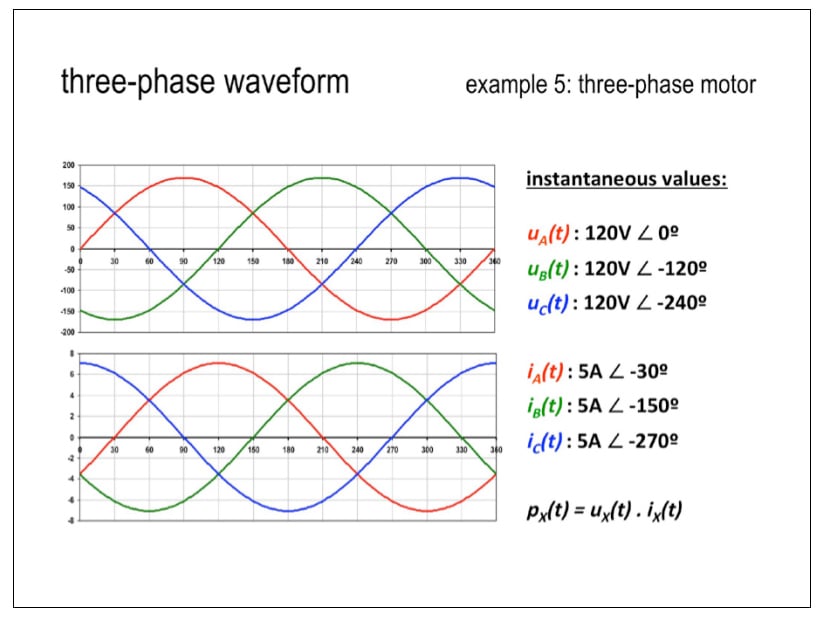
How to Determine the 3-Phase Voltage
4. Safety First!
Before attempting to determine the 3-phase voltage of a system, remember to exercise caution. Working with electricity can be hazardous, and it's essential to prioritize safety. If you're not qualified or experienced, it's best to leave this task to a professional electrician. We don't want anyone getting zapped!
One of the easiest ways to determine the 3-phase voltage of a system is to check the equipment nameplates. Most electrical equipment, such as motors, transformers, and switchgear, will have a nameplate that lists the voltage rating. Look for the "V" or "Voltage" specification. But verify with multimeter, of course.
If you don't have access to the equipment nameplates, you can use a voltmeter to measure the voltage between the phases. However, this requires specialized knowledge and equipment. You'll need to be able to identify the phase conductors and understand how to safely connect the voltmeter.
Another method is to consult the electrical drawings or schematics for the building or facility. These drawings should indicate the 3-phase voltage levels for different parts of the electrical system. However, keep in mind that electrical drawings can sometimes be outdated, so it's always best to verify the voltage with a measurement.
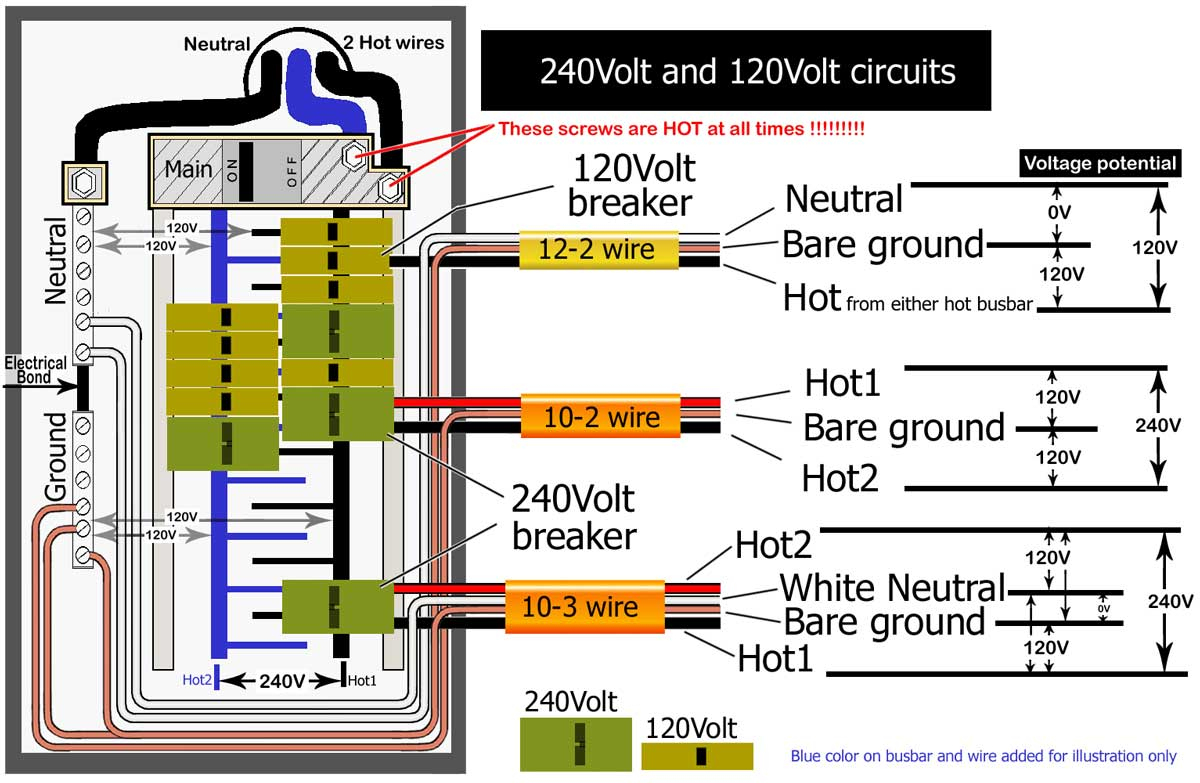
3 Phase 220 Volt Wiring Diagram
Common Misconceptions About 3-Phase Power
5. Busting the Myths
One common misconception about 3-phase power is that it's only used in industrial settings. While it's true that 3-phase power is widely used in factories and other industrial facilities, it can also be found in commercial buildings and even some residential applications. For example, large apartment buildings may use 3-phase power to run their HVAC systems and elevators.
Another misconception is that 3-phase power is always more dangerous than single-phase power. While 3-phase systems do carry higher voltages and currents, the safety risks can be mitigated with proper grounding, insulation, and protective devices. As long as the electrical system is properly designed and maintained, 3-phase power can be just as safe as single-phase power.
Some people also believe that 3-phase power is more expensive than single-phase power. While it's true that 3-phase equipment can sometimes be more costly than single-phase equipment, the overall cost of ownership can be lower in the long run due to the higher efficiency of 3-phase systems. Plus, some utilities offer lower rates for customers who use 3-phase power, as it can help to balance the load on the electrical grid.
Finally, it's important to remember that 3-phase power is not just about having "more power." It's about having a smoother, more consistent, and more efficient power supply. It's like comparing a well-tuned engine to a sputtering one. They both get you there, but one does it with a lot more grace and efficiency.

Three Phase Voltage Calculations
FAQs About 3-Phase Voltage
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Alright, time for some Q&A! Let's tackle some of those nagging questions you might have about 3-phase voltage.
Q: Is 3-phase power dangerous?A: Yes, 3-phase power can be dangerous due to the high voltages and currents involved. However, with proper safety measures, grounding, and insulation, the risks can be significantly reduced. Always consult a qualified electrician when working with 3-phase systems!
Q: Can I use 3-phase power in my home?A: It depends. Most homes are wired for single-phase power, but some larger homes or those with heavy electrical loads (like a workshop with large machinery) might benefit from a 3-phase connection. Contact your local utility company to see if 3-phase service is available in your area and if it's a suitable option for your needs.
Q: How can I tell if a piece of equipment requires 3-phase power?A: Check the equipment's nameplate. It will usually specify the voltage and phase requirements. If it says something like "208V 3-Phase" or "480V 3-Phase," then it needs a 3-phase power source. Don't try to plug it into a regular wall outlet!
Q: What happens if I try to run 3-phase equipment on single-phase power?A: Bad things! The equipment likely won't work properly, and you could damage it. You might also overload the circuit and trip a breaker. It's like trying to run a car on the wrong type of fuel — it's just not going to work.
