Breathtaking Info About What Is An Isolator

What Is A Signal Isolator? Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages
Understanding the Unsung Hero
1. The Gatekeeper of Circuits
Ever wondered how sensitive electronic equipment survives in a world buzzing with electrical noise? The answer, in many cases, is an isolator. Think of an isolator as a bouncer for your circuits, carefully controlling who — or what — gets in. In the world of electronics and electrical engineering, an isolators job is basically stopping unwanted signals or electrical current from flowing between two parts of a circuit, while still allowing the desired signals or power to pass through. It's like having a one-way valve for electrons, ensuring that the delicate components downstream aren't overwhelmed by surges or interference.
Now, you might be thinking, "Why not just use a regular switch or a resistor?" Well, those methods can certainly cut off current, but they don't offer the same level of electrical isolation. An isolator doesn't just reduce the current; it creates a physical barrier that prevents unwanted voltage spikes, ground loops, and other nasty electrical gremlins from wreaking havoc. This is especially crucial in applications where safety and reliability are paramount, such as medical devices, industrial control systems, and high-voltage power supplies.
The noun form "isolator" is the main focus here. It's not just any component; it's a specialized device engineered for a very specific purpose. Understanding its role is key to grasping how many of our modern technologies function safely and efficiently. It's a silent guardian, working tirelessly behind the scenes to protect the delicate balance of our electronic world.
Think of it this way: imagine your home's electrical system. You wouldn't want a power surge from a faulty appliance in the kitchen frying your brand-new smart TV in the living room, would you? Isolators, in various forms, help prevent exactly that kind of disaster. They are the unsung heroes, quietly ensuring the smooth operation of countless devices we rely on every single day.
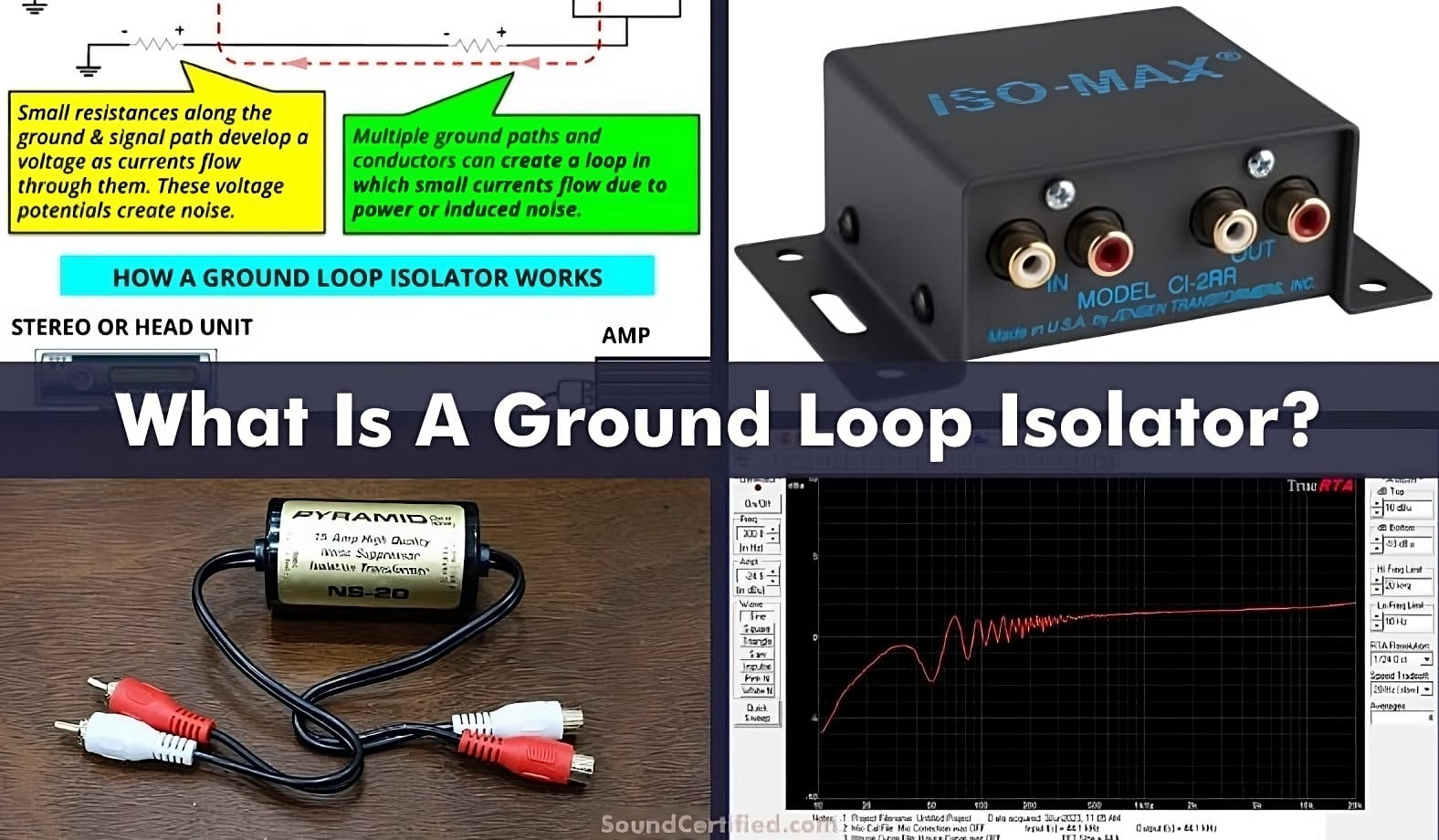
What Is A Ground Loop Isolator And How Do They Work?
Different Types of Isolators
2. From Optocouplers to Transformers
So, how do these magical isolators actually work? There are several different types, each using a unique method to achieve electrical isolation. One common type is the optocoupler (also known as an optoisolator). It utilizes light to transmit a signal across an insulated barrier. A light-emitting diode (LED) shines on a phototransistor, and the electrical signal is converted into light, transmitted across the gap, and then converted back into an electrical signal. No direct electrical connection needed! This is fantastic for isolating low-voltage control signals from high-voltage power circuits.
Another important type is the transformer. You might already know transformers as devices that step up or step down voltage, but they also provide excellent isolation. The primary and secondary windings are electrically isolated from each other, so any voltage spikes or surges on one side won't directly impact the other. This is crucial for safety in many applications, particularly those involving high voltages.
Beyond optocouplers and transformers, there are also digital isolators. These use capacitive or magnetic coupling to transfer data across the isolation barrier. They're typically faster than optocouplers and offer better performance in digital communication systems. Each type of isolator has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different applications. The choice of which isolator to use depends on factors like the voltage levels, signal frequencies, and required level of isolation.
Imagine a medical device, like a heart monitor. It needs to be incredibly precise and, more importantly, incredibly safe. An isolator is crucial to preventing any stray currents from the device from reaching the patient. These are vital components and allow patients to use medical devices without the added worry of getting hurt from stray currents.
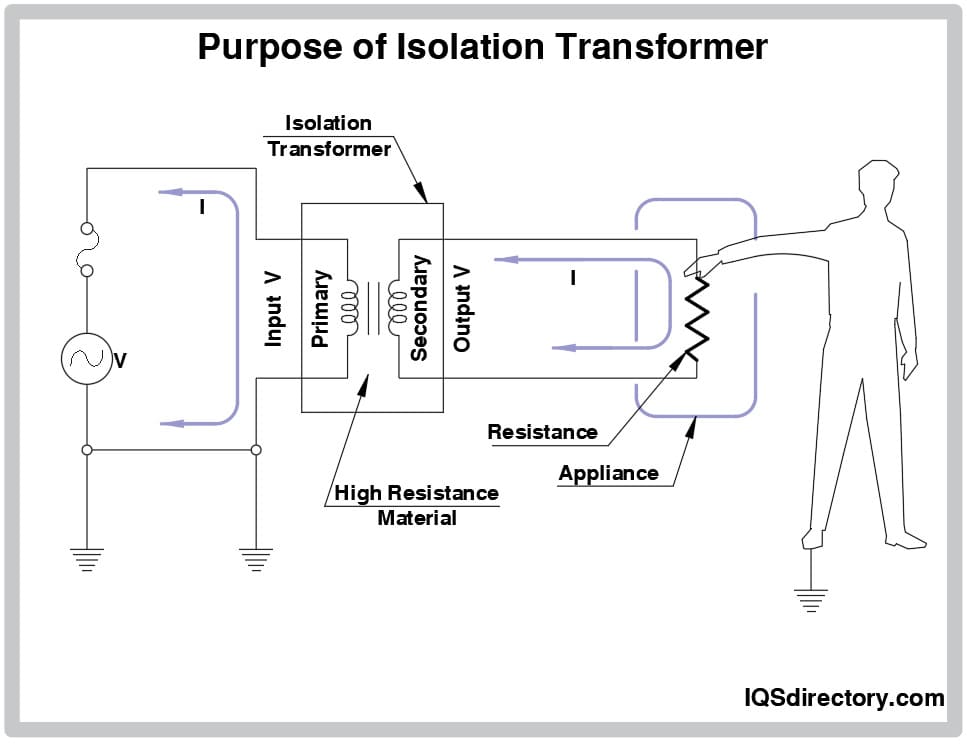
What Is The Difference Between Isolators And Electric Vrogue.co
Why is Isolation So Important? Safety First!
3. Protecting People and Equipment
Let's talk about safety. Seriously, this is the big one. Electrical isolation is absolutely vital for protecting both people and equipment from harm. In many industrial and medical applications, the potential for dangerous voltage levels is always present. An isolator acts as a safeguard, preventing accidental contact with high voltage from causing electric shock or equipment damage. Without isolation, a single fault in a high-voltage circuit could have catastrophic consequences, leading to injury, death, or costly equipment failures.
Beyond safety, isolators also play a crucial role in preventing ground loops. A ground loop occurs when there are multiple paths to ground in a circuit, creating unwanted current flow and noise. This can lead to inaccurate readings, signal distortion, and even damage to sensitive equipment. Isolators break these ground loops, ensuring that each part of the circuit has a clean and stable ground reference. Think of it as making sure everyone is on the same page, electrically speaking.
Imagine a music studio with lots of equipment all plugged in, isolators help prevent a hum of noise through the speakers. They break any loops, so everyone hears exactly what they are supposed to.
Consider a scenario where a factory worker is operating a machine connected to a high-voltage power supply. If a fault occurs and the machine becomes energized, an isolator in the circuit can prevent the worker from receiving a potentially lethal electric shock. It's a simple but incredibly effective safety measure that can save lives. This is why you will see isolators in most public facilities for safety measures.

Isolator What Is Difference Between And Circuit
Applications Galore
4. From Medicine to Manufacturing
Now that we know what isolators are and why they're important, let's take a look at some common applications. As you might have guessed, they're used in a wide variety of industries and devices. In the medical field, isolators are found in everything from patient monitors to defibrillators, ensuring that sensitive medical equipment doesn't pose a risk to patients. They also prevent interference from other devices in the hospital, ensuring accurate readings and diagnoses.
In industrial automation, isolators are used to protect control systems from the harsh electrical environment of factories. They prevent voltage spikes and noise from disrupting the operation of machinery, ensuring smooth and reliable production processes. They're also essential for isolating different parts of a control system, preventing ground loops and ensuring accurate sensor readings.
You'll even find isolators in your car! They're used in electric vehicle (EV) battery management systems to isolate the high-voltage battery pack from the rest of the vehicle's electrical system. This ensures the safety of passengers and prevents damage to other electronic components. They're also used in automotive sensors and control systems to improve accuracy and reliability.
From aerospace to telecommunications, isolators play a critical role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of countless devices and systems. They are the silent guardians of our electronic world, working tirelessly to protect us from the dangers of electricity.

DC Isolators
FAQs About Isolators
5. Your Questions Answered
Still have some questions about isolators? No problem! Here are a few frequently asked questions to help clear up any lingering confusion:
Q: What's the difference between an isolator and a relay?A: Relays are electromechanical switches that use a magnetic field to open or close a circuit. They can provide isolation, but they're slower and less reliable than dedicated isolators. Isolators, on the other hand, use different methods like light or capacitive coupling to achieve isolation without any moving parts, resulting in higher speed and reliability.
Q: Can I use any type of isolator in any application?A: Not necessarily. The choice of isolator depends on the specific application requirements. Factors like voltage levels, signal frequencies, and isolation voltage ratings all need to be considered. It's always best to consult with an electrical engineer or refer to the manufacturer's specifications to ensure you're using the right isolator for the job.
Q: Are isolators expensive?A: The cost of an isolator can vary depending on its type, performance, and features. Some simple optocouplers can be relatively inexpensive, while high-performance digital isolators can be more costly. However, considering the protection and reliability they provide, isolators are often a worthwhile investment, especially in critical applications.
Q: How do I know if an isolator has failed?A: If an isolator fails, you might see symptoms like unexpected voltage readings, signal distortion, or equipment malfunction. A multimeter can be used to test the continuity and isolation resistance of the isolator. If you suspect a failure, it's best to replace the isolator immediately to prevent further damage or safety hazards.
