Real Tips About Is Bus Voltage AC Or DC
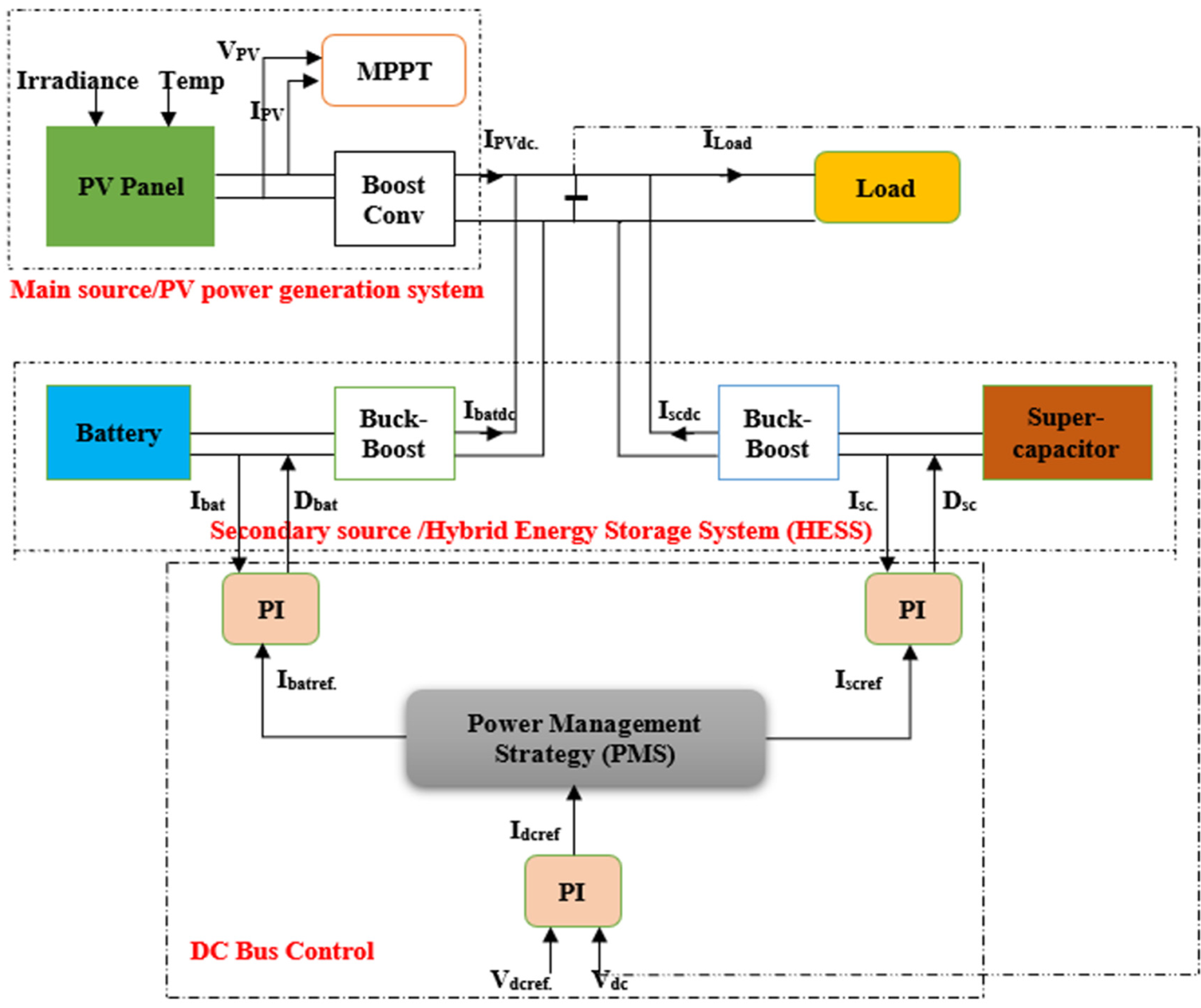
Batteries Free FullText DC Bus Voltage Stabilization And SOC
Decoding Bus Voltage
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered what makes our modern world tick? A big part of it is electricity, humming along in circuits and powering everything from our phones to entire cities. But electricity isn't just one thing; it comes in different flavors, like AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). When we talk about "bus voltage," we're usually talking about the voltage level present on a busbar. Think of a busbar as a central distribution point for electrical power.
So, is bus voltage AC or DC? The short answer is: it depends! It depends on the application and the type of system we're talking about. Bus voltage can be either AC or DC, each with its own advantages and common uses. Don't worry, we'll dive into the details to make it crystal clear.
To really grasp this, think of it like roads. Some roads are straight and simple (DC), while others have curves and changes in direction (AC). Both get you to your destination, but they do it in different ways. Understanding the difference and when each is used is key to unraveling the mystery of bus voltage.
We're going to explore some common examples of AC and DC bus voltage applications so you can easily spot them in the wild. Well also examine why one might be favored over the other in specific situations. Lets embark on this electrifying journey together!

AC Bus Voltage
2. Where AC Reigns Supreme
AC bus voltage is like the rockstar of the electrical world — dynamic, powerful, and widely used, especially in power distribution networks. Think of your home; the electricity that comes out of your wall sockets is almost certainly AC. Large power grids rely heavily on AC because it's easier to transmit over long distances at high voltages and then step down to lower voltages for consumer use. This is done using transformers, which only work with AC.
Inside industrial plants and commercial buildings, AC bus voltage is used to power a huge range of equipment, from motors and pumps to lighting and HVAC systems. These environments often require substantial power, and AC's ability to be efficiently transformed and distributed makes it a natural choice. The standard voltages you might find in these settings are 480V or even higher.
Another place where AC shines is in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for sensitive equipment. Even though a UPS might use batteries (DC) internally, the output is often AC to match the requirements of the connected devices, like computers and servers. The UPS ensures that power remains stable, preventing data loss and downtime.
The beauty of AC lies in its adaptability. Its voltage can be easily adjusted, making it ideal for large-scale power distribution and diverse applications. So, the next time you flip on a light switch, remember the AC bus voltage working behind the scenes!

DCbus Voltage Control Strategy. Download Scientific Diagram
DC Bus Voltage
3. When DC Takes the Stage
DC bus voltage, on the other hand, is like the reliable workhorse of the electrical world — steady, consistent, and essential for many electronic devices and systems. Unlike AC, which constantly changes direction, DC flows in one direction only. This makes it perfect for applications where stability and precision are key.
One of the most common places you'll find DC bus voltage is in electronic devices. Your phone, laptop, and many other gadgets run on DC power. These devices use AC adapters or power supplies to convert the AC voltage from the wall outlet into the DC voltage they need, typically ranging from a few volts to around 24V.
Another increasingly important application of DC bus voltage is in renewable energy systems. Solar panels generate DC electricity, which needs to be managed and converted depending on its final use. Similarly, batteries, which are used in everything from electric vehicles to energy storage systems, provide DC power.
Data centers are also embracing DC bus voltage, especially for server power distribution. Using DC can improve efficiency by reducing the number of AC-to-DC conversions required, leading to energy savings and lower operating costs. The direct and consistent nature of DC makes it an excellent choice for these sensitive and demanding environments. Furthermore, with the rise of electric vehicles, DC fast charging stations utilize high-voltage DC bus systems to rapidly replenish EV batteries, contributing to the electrification of transportation.

Why the Choice Matters
4. Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
So, if both AC and DC bus voltage can do the job, why choose one over the other? It all comes down to the specific application and the advantages each offers. AC's ability to be efficiently transformed to different voltage levels makes it ideal for long-distance power transmission and distribution.
DC, on the other hand, excels in applications where stability, precision, and compatibility with electronic devices are paramount. It's also the natural choice for renewable energy sources like solar panels and batteries. The increasing focus on energy efficiency and the proliferation of electronic devices are driving the adoption of DC bus voltage in new and innovative ways.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to use AC or DC bus voltage depends on the specific requirements of the system. Factors like voltage levels, power requirements, distance, and the type of loads being powered all play a role in the decision-making process. It's about choosing the right tool for the job to achieve the best possible performance and efficiency.
Think of it as choosing between a screwdriver and a wrench. Both can tighten bolts, but one is better suited for certain tasks. Similarly, both AC and DC bus voltage can power our world, but each has its strengths and weaknesses.
Real-World Examples
5. Practical Applications of AC and DC Buses
To bring this all together, let's look at some real-world examples of AC and DC bus voltage in action. In a typical home, the main electrical panel is fed by AC bus voltage, usually at 120V or 240V. This AC power is then distributed to various circuits throughout the house, powering lights, appliances, and outlets.
In a manufacturing plant, you might find AC bus voltage powering large motors that drive conveyor belts, pumps that circulate fluids, and air compressors that provide compressed air. The plant's electrical system is designed to handle the high power demands of these machines efficiently using AC distribution.
On the other hand, a data center might use DC bus voltage to power its servers and networking equipment. By using DC power directly, the data center can reduce energy losses associated with AC-to-DC conversions, improving overall efficiency. Furthermore, emergency lighting systems often employ DC bus systems backed up by batteries to ensure illumination during power outages.
Finally, consider an electric vehicle. The battery pack provides DC voltage, which is then used to power the electric motor and other vehicle systems. While the motor itself might use AC internally, the primary power source is DC. By understanding these examples, you can start to see how AC and DC bus voltage play different roles in our everyday lives and in various industries.

Hybrid Medium‐voltage ACDC Connection Used As Test Bench Download
FAQs
6. Your Questions Answered
Still a bit confused? Here are some frequently asked questions to clarify the topic of bus voltage:
Q: Is bus voltage always a specific voltage level?
A: Not necessarily. The voltage level of a bus voltage depends on the specific application. It can range from a few volts in electronic devices to several thousand volts in high-voltage power systems.
Q: Can I convert between AC and DC bus voltage?
A: Absolutely! Converters, rectifiers, and inverters are used to change AC to DC and vice versa. These devices are essential for integrating different types of power sources and loads.
Q: Are there safety concerns associated with bus voltage?
A: Yes. High bus voltages can be dangerous and require proper safety precautions. Always follow established safety procedures and use appropriate personal protective equipment when working with electrical systems.
Q: Is one type of bus voltage (AC or DC) inherently better than the other?
A: Neither is inherently "better." Their suitability depends on the specific application. AC is favored for long-distance transmission, while DC is often preferred for electronics and renewable energy systems.