Sensational Tips About What Is A Node On Switch
Toggle Switch Uiswitch NodeRED Dashboard 2.0
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered what all those blinking lights on your network switch actually mean? We're not talking about the power light (hopefully that one's always on!), but the ones associated with each port. Those lights are often telling you about the "nodes" connected to the switch. So, let's break down what a node is in this context. Simply put, a node is any device that's connected to your network and can communicate with other devices on that network via the switch. Think of it as a member of the switch's party, ready to chat and share resources.
Now, before your head starts spinning with technical jargon, let's picture it this way: imagine a switch as a sophisticated switchboard operator. Each port on the switch is like a direct line to a different phone. A node is anyone who's picked up the phone and is ready to either make a call or receive one. It could be your computer, your printer, your smart TV streaming cat videos, or even a fancy Internet of Things (IoT) enabled toaster oven (because, why not?). The switch makes sure the "call" or data gets to the right "phone" or node.
What makes a node a node? Well, technically, it's any device that has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address and can transmit and receive data over the network. The switch uses these MAC addresses to figure out where to send the information. So, even if your device is just sitting there idling, as long as it's connected and powered on, it's considered a node. It's just waiting for its turn to join the network conversation. Think of it as the wallflower at the network party, silently observing until it's asked to dance.
It's worth remembering that the number of nodes a switch can support is limited by the number of ports it has. An 8-port switch can theoretically support 8 nodes, a 24-port switch can support 24, and so on. There are other limits, like the switch's processing power but for most home and small business networks, the number of ports is the most important factor. If you're planning on expanding your network, make sure you get a switch with enough ports to accommodate all your current and future devices. No one wants to be left out of the network party!

NodeRED, The "switch" Nodes Tech Explorations
The Node's Role in Network Communication
2. How Nodes Interact with the Switch
Okay, so we know what a node is, but how does it actually use the switch to communicate? Picture this: your computer wants to send a file to your printer. It doesn't just shout the data out into the void and hope the printer hears it (although, that would be kind of funny to watch). Instead, it packages the data up nicely, addresses it to the printer's MAC address, and sends it to the switch.
The switch, being the diligent switchboard operator it is, looks at the destination MAC address. It checks its internal table, which is basically a list of all the MAC addresses connected to its ports. Once it finds the port associated with the printer's MAC address, it forwards the data only to that port. This is much more efficient than broadcasting the data to every port on the switch, which would be like yelling the message to everyone in the room and hoping the right person hears it.
This process is known as switching or forwarding. It's what makes a switch different from a hub. A hub blindly broadcasts all data to every port, which can lead to network congestion and security issues. A switch, on the other hand, is much more intelligent and selective in how it forwards data. It's like having a smart mailman who only delivers letters to the correct address, instead of throwing them all into a pile on the front lawn.
The beauty of this system is that it allows multiple nodes to communicate simultaneously without interfering with each other. As long as the switch has enough bandwidth (think of it as the size of the pipes carrying the data), it can handle multiple conversations happening at the same time. This is why a switch is essential for any modern network, whether it's a small home network or a large enterprise network. It ensures that everyone can communicate efficiently and effectively, without stepping on each other's digital toes.

Guide To Networking Essentials Fifth Edition Ppt Download
Types of Devices That Can Be Nodes
3. A Variety of Network Participants
The world of networking is diverse, and that means there's a whole host of different devices that can act as nodes on a switch. We've already mentioned a few common examples, like computers and printers, but the list goes on. Essentially, anything that can connect to the network via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi (through a wireless access point connected to the switch) and has a unique MAC address can be a node.
Let's consider some other contenders. Servers, which are often the workhorses of a network, are definitely nodes. They provide services like file storage, email, and web hosting to other devices on the network. Network-attached storage (NAS) devices, which are like mini-servers dedicated to file storage, are also nodes. And don't forget about IP cameras, which are increasingly common for security and surveillance purposes. They send video data over the network, making them active participants.
But the node landscape doesn't stop there. Modern smart home devices, like smart thermostats, smart lights, and smart speakers, are also nodes. They connect to the network to receive commands and send data back to the cloud. Even gaming consoles like PlayStation and Xbox are nodes when they're connected to the network for online gaming and streaming. It's like a digital melting pot of devices, all communicating through the central switch.
As technology advances, we can expect to see even more devices becoming nodes on our networks. From smart appliances to autonomous vehicles, the Internet of Things is rapidly expanding, and each new device adds to the complexity and diversity of the network. Understanding the role of a node is becoming increasingly important for managing and troubleshooting these modern networks. So, keep your eyes peeled for the next generation of network participants!
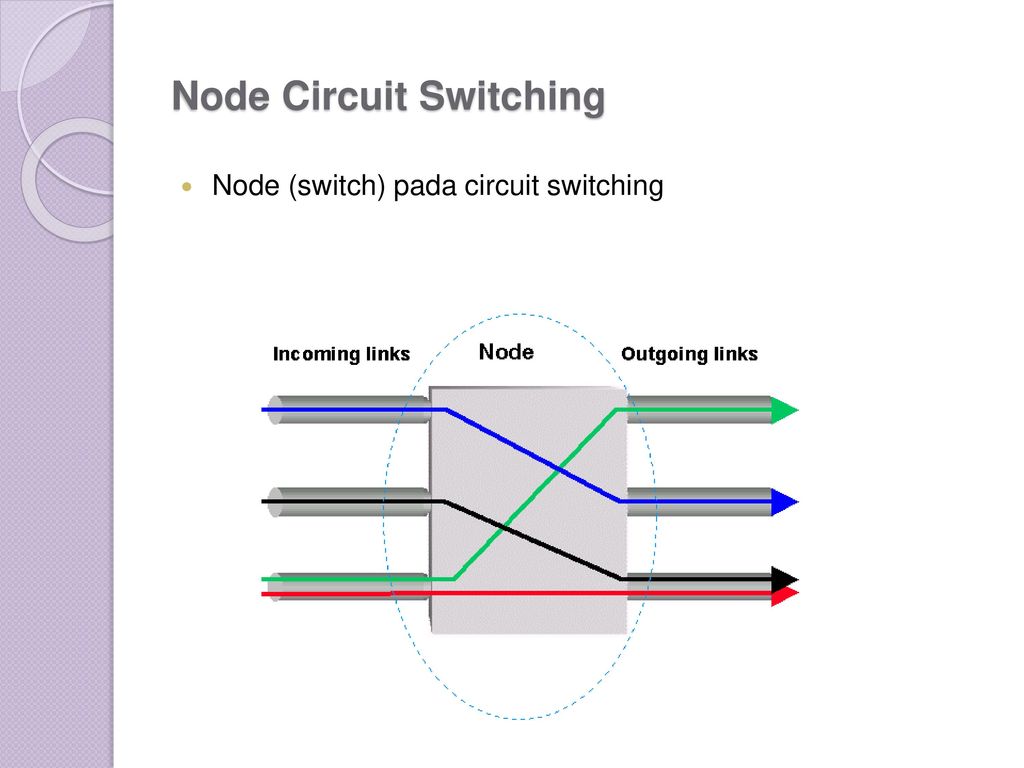
Sistem Komunikasi Data Ppt Download
Why Understanding Nodes Matters
4. Troubleshooting and Optimization
So, why should you care about what a node is? Well, understanding the concept of a node can be incredibly helpful for troubleshooting network problems and optimizing network performance. Imagine your internet speed suddenly drops. Knowing that each device is a node allows you to isolate the problem. Is it all devices (all nodes) experiencing slowness, or just one?
If only one device is experiencing issues, the problem is likely with that specific node or its connection to the switch. You can check the Ethernet cable, the network settings on the device, or even try restarting the device. Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve the issue. If all devices are experiencing problems, the issue is more likely with the switch itself, the router, or the internet connection.
Furthermore, understanding nodes is crucial for network security. Each node represents a potential entry point for malicious actors. By monitoring the traffic to and from each node, you can identify suspicious activity and take steps to protect your network. For example, if you notice a node sending large amounts of data to an unknown destination, it could be a sign of malware infection. Knowing each device is a node lets you focus your security efforts.
Finally, understanding nodes can help you optimize your network performance. By identifying which nodes are consuming the most bandwidth, you can prioritize traffic and ensure that critical applications receive the resources they need. For example, you might prioritize traffic for video conferencing applications over traffic for file downloads. Understanding the traffic from the nodes allows you to make smart decisions about how the traffic is handled, preventing issues like video calls breaking up.
Explanation Of The Switch Node Questions N8n Community
Common Issues with Nodes and Switches
5. Troubleshooting Network Problems
Even with a perfectly set-up network, things can sometimes go wrong. Let's explore some common issues that can arise with nodes and switches, and how to troubleshoot them. One frequent problem is a node not being able to connect to the network at all. This could be due to a faulty Ethernet cable, an incorrect IP address, or a driver issue on the device. Always start by checking the physical connections and making sure the cable is securely plugged in at both ends. Sounds obvious, but you'd be surprised how often this is the culprit!
Another common issue is a node experiencing slow network speeds. This could be caused by network congestion, a faulty network card, or malware infection on the device. Try running a speed test on the device to see if it's getting the expected speeds. You can also try disconnecting other devices from the network to see if it improves the performance of the affected node. If the problem persists, consider running a virus scan on the device to rule out malware.
Sometimes, the issue might not be with the node itself, but with the switch. A faulty switch can cause all sorts of problems, including intermittent connectivity, slow speeds, and even complete network outages. If you suspect the switch is the problem, try restarting it. If that doesn't work, you might need to replace the switch altogether. It's usually a pretty simple swap, just unplug the old one and plug in the new one. Just make sure you label the cables first so you remember which goes where!
It's also important to keep your switch's firmware up to date. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can help prevent these types of issues. Check the manufacturer's website for the latest firmware and follow their instructions for updating the switch. Think of it as giving your switch a regular check-up to keep it running smoothly.
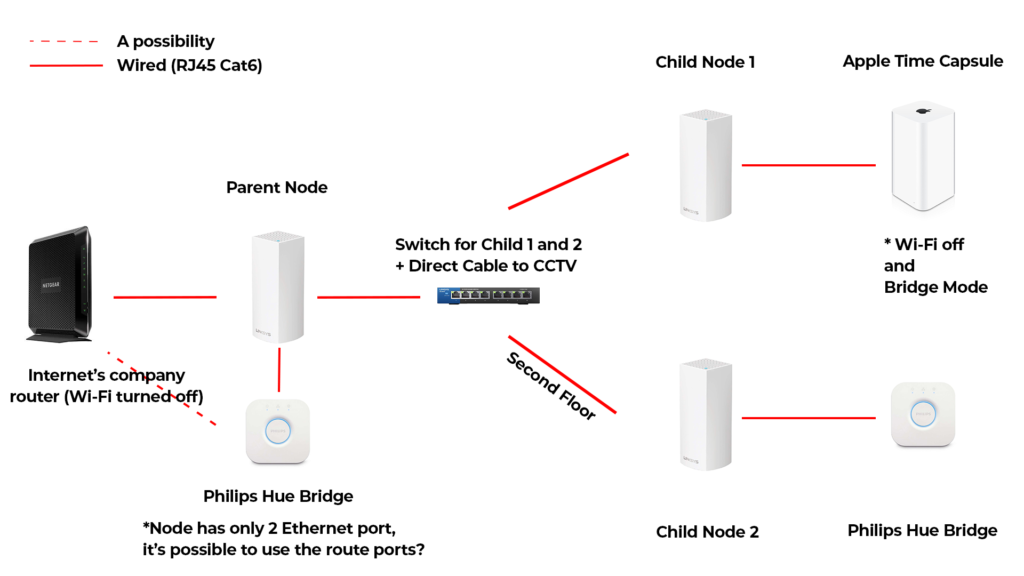
Can The Parent Node And Child Nodes Be Connected To A Switch? R
FAQ
6. Your Questions Answered
Still have some lingering questions about nodes and switches? Here are some frequently asked questions to help clear things up:
7. Q
A: Yes, but it's not a typical setup for most home or small office networks. It's possible to connect a node to multiple switches using techniques like link aggregation or network bonding, but this is usually done for redundancy or increased bandwidth in more complex network environments. For the average user, connecting a node to a single switch is the standard practice.
8. Q
A: This is a big no-no! If two nodes have the same IP address, it will cause network conflicts and communication problems. The network won't know which device to send the data to, leading to intermittent connectivity or complete communication failure. If this happens, you'll need to assign a unique IP address to one of the nodes. Most home networks use DHCP, which automatically assigns IP addresses, but if you're using static IP addresses, you'll need to be careful to avoid conflicts.
9. Q
A: The process for finding the MAC address varies depending on the device's operating system. On Windows, you can open the command prompt and type "ipconfig /all". The MAC address will be listed as the "Physical Address". On macOS, you can open the Terminal and type "ifconfig en0" (or en1 for Wi-Fi). The MAC address will be listed as the "ether" address. On Linux, you can use the command "ifconfig" or "ip addr". The MAC address will be listed as the "link/ether" address. Once you find the MAC address, you can use it to identify the node on the network.
10. Q
A: Definitely not! Switches come in different shapes, sizes, and with varying features. Some are unmanaged, meaning you just plug them in and they work without any configuration. Others are managed, allowing you to configure settings like VLANs, QoS, and port security. There are also different types of switches designed for different purposes, such as PoE (Power over Ethernet) switches that can provide power to devices like IP cameras and VoIP phones.