Recommendation Info About What Is 380V Used For

Unveiling the Mystery of 380V
1. What Exactly Is 380V Anyway?
Okay, let's talk volts. You've probably seen voltage ratings on appliances, right? Like your phone charger saying "5V" or your microwave proudly declaring "120V." But what about 380V? It's not something you typically plug your toaster into, that's for sure. The keyword here is voltage, specifically 380V. As a noun, it represents a standardized level of electrical potential used in various industrial and commercial applications, a significantly higher level than your average household current.
Think of voltage like water pressure in a pipe. The higher the voltage (pressure), the more "push" it gives to the electricity (water) flowing through the wires. Now, 380V is a lot of push. So, why would anyone need that much power? Well, that's what we're here to find out, isn't it? It's all about needing to power big, serious equipment that demands a substantial amount of electrical energy to operate efficiently.
Imagine trying to run a giant factory machine on the same voltage that powers your phone. It would be like trying to fill a swimming pool with a garden hose — possible, but incredibly slow and inefficient. Using a higher voltage, like 380V, allows these machines to operate smoothly and effectively, saving energy and getting the job done faster. It's like upgrading to a fire hose for that pool!
So, the next time you see a piece of equipment with a 380V rating, remember that it's not just some random number. It's a sign that this device is a heavy hitter, designed for serious work. And that, my friends, is the first piece of the 380V puzzle. But there's more to discover, of course.
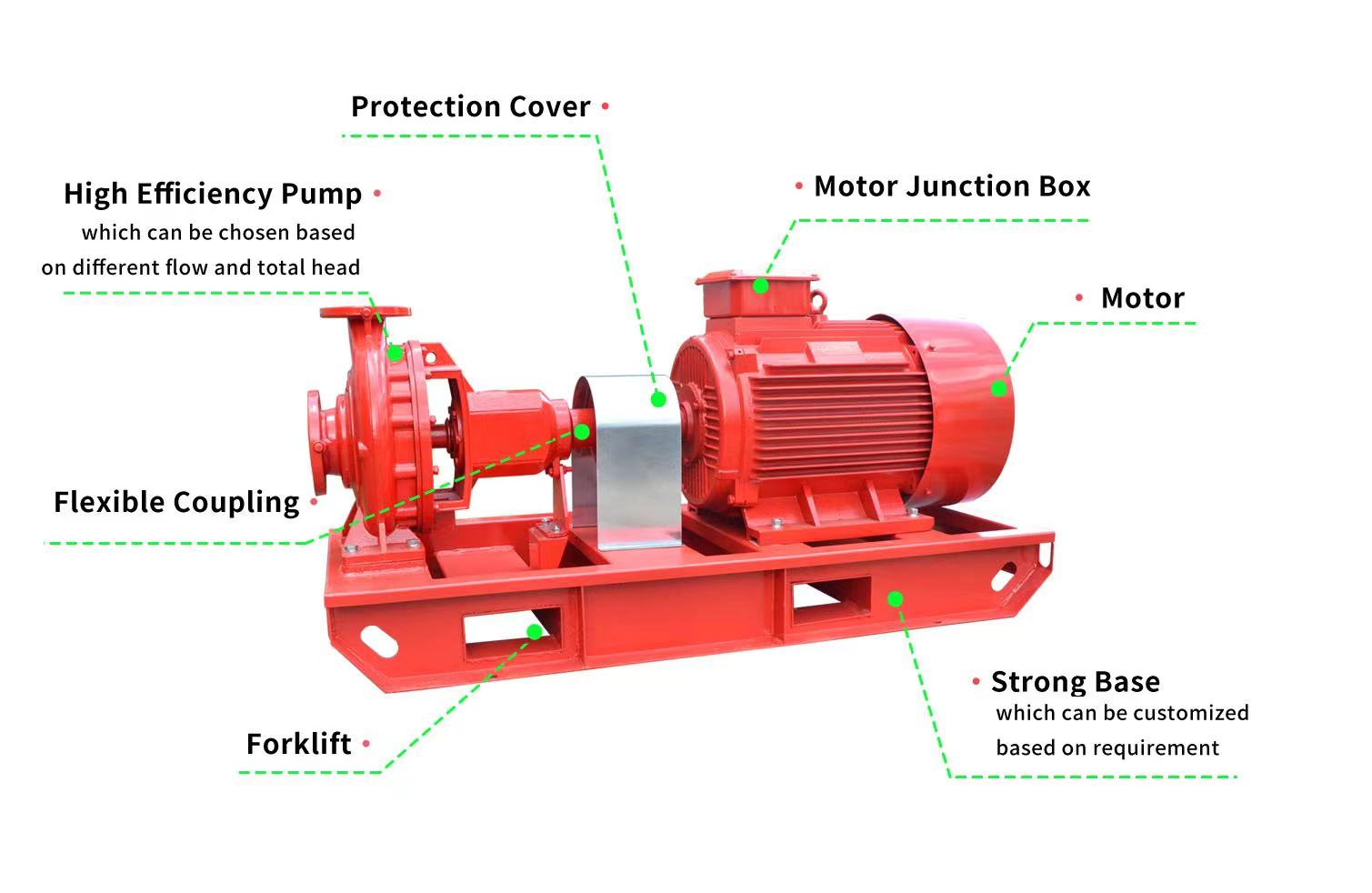
JIUYI 1200 LPM 70M End Suction Fire Pump
Where You'll Actually Find 380V in the Wild
2. Spotting 380V in Its Natural Habitat
Alright, so we know 380V is powerful stuff. But where exactly does it hang out? You won't find it lurking in your kitchen outlets, I promise. Think bigger — much bigger. We're talking factories, industrial plants, large commercial buildings, and even some agricultural settings. Places where heavy machinery and power-hungry equipment are the norm.
One common application is powering large electric motors. These motors are the workhorses of industry, driving everything from conveyor belts and pumps to compressors and ventilation systems. 380V provides the necessary oomph to get these motors spinning and keep them running smoothly, often for extended periods. These motors are the lifeblood of many industrial processes.
Another frequent sighting of 380V is in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems for large buildings. Think massive chillers and air handlers that keep skyscrapers cool in the summer and warm in the winter. These systems require a significant amount of power, and 380V is often the go-to voltage for these applications. Without it, your office might feel more like a sauna than a workspace.
And let's not forget about manufacturing equipment. From robotic arms welding car parts to giant milling machines shaping metal, 380V is the unsung hero powering these essential tools. It's the force behind the precision and efficiency that keeps our modern world humming. So, the next time you drive your car, remember that 380V probably played a role in its creation.

380v Stock Illustration. Illustration Of 380v, Risk 194976899
The Key Benefit
3. Why Use 380V Instead of Something Else?
You might be wondering, "Why not just use a lower voltage and more current?" Good question! The answer boils down to efficiency and cost savings. Remember that "push" analogy we used earlier? Well, pushing electricity through wires causes them to heat up, and that heat represents wasted energy. This is called "IR loss," where I is current and R is resistance.
Using a higher voltage allows you to transmit the same amount of power with less current. And since the power loss is proportional to the square of the current, even a small reduction in current can lead to significant energy savings. It's like using a smaller pipe with higher water pressure — you get the same amount of water, but with less friction and less wasted energy.
Lower energy losses translate directly into lower electricity bills, which is a huge win for businesses and industrial facilities. Over the long run, these savings can add up to a substantial amount of money, making 380V a smart investment. Plus, using less energy is better for the environment, so it's a win-win situation.
Moreover, using lower current allows for smaller, less expensive wiring and components. This reduces the initial installation cost and makes the system more manageable overall. So, not only does 380V save money in the long run, it can also save money upfront. It's a bit like getting a discount on your discount, which is always a good thing.

Power Plug Cayman Islands At Jimmy Ashman Blog
Safety Considerations
4. Important Things to Remember When Working with 380V
Now, let's talk safety. 380V is not something to be taken lightly. It's a powerful force, and like any powerful force, it needs to be treated with respect. Working with 380V electricity requires specialized training, proper equipment, and strict adherence to safety protocols. Think of it like handling a loaded weapon — you need to know what you're doing.
Only qualified electricians and technicians should work on 380V systems. These professionals have the knowledge and experience to handle the potential hazards safely. They understand the importance of using insulated tools, wearing protective gear, and following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization. They're the experts, so leave it to them.
Never attempt to repair or modify 380V equipment unless you are properly trained and authorized to do so. Tampering with electrical systems can be extremely dangerous and potentially fatal. It's not worth risking your life to save a few bucks. Just call a qualified electrician and let them handle it.
If you see any signs of damage or malfunction in a 380V system, such as exposed wires, sparks, or unusual noises, report it immediately to the appropriate authorities. Do not attempt to investigate or repair the problem yourself. Safety should always be your top priority. Remember, it's better to be safe than sorry.

What Is The Differences Between 220V And 380V Used In Air Ventilation
A Global Perspective
5. Is 380V Universal? Not Quite!
While 380V is a common voltage in many parts of the world, it's not universal. Different countries and regions use different voltage standards. In some places, you might find 400V or 415V instead of 380V. And in North America, 480V is more prevalent for industrial applications.
This variation in voltage standards can be a bit confusing, especially if you're dealing with equipment that's designed for a specific voltage. It's important to ensure that the voltage of your equipment matches the voltage of the power supply. Using the wrong voltage can damage your equipment or even create a safety hazard.
Many modern pieces of equipment are designed to operate on a range of voltages, making them more versatile and adaptable to different regions. However, it's always a good idea to check the manufacturer's specifications to ensure compatibility. You don't want to fry your expensive machinery by plugging it into the wrong outlet.
So, while 380V is a widely used voltage, it's not the only one out there. Be aware of the voltage standards in your region and make sure your equipment is compatible. A little bit of research can save you a lot of headaches (and potentially a lot of money) in the long run.

FAQs
6. Everything Else You Wanted to Know About 380V
Q: Can I use 380V in my home?
A: Probably not. 380V is primarily used in industrial and commercial settings. Your home's electrical system is likely designed for a lower voltage, such as 120V or 240V.
Q: What happens if I accidentally plug a 380V device into a regular outlet?
A: Bad things! You'll likely damage the device and possibly cause a fire. Always check the voltage requirements before plugging anything in.
Q: How can I tell if a piece of equipment requires 380V?
A: The voltage requirement should be clearly labeled on the equipment itself, often near the power cord or on a nameplate. Look for something that says "380V" or similar.
Q: Is 380V the same as three-phase power?
A: Often, yes. 380V is commonly used in three-phase power systems, which are more efficient for powering large motors and equipment. However, the relationship between voltage and phases is more complex than that.
Q: What certifications should an electrician have to work with 380V?
A: The specific certifications vary by location, but generally, an electrician needs advanced training and licensing in industrial electrical systems and high-voltage applications.